You might wonder, how long does it take to charge an electric car? The answer depends on the charging method and your EV model. For example, charging at home with a standard outlet can take over 40 hours, while a home charger may fill most EV batteries in 4 to 10 hours. Public DC fast chargers add up to 80% in just 20 to 60 minutes. Most EV owners find charging at home overnight convenient and stress-free. Here’s a quick look at typical charging times:
Charging Method | Power Output | Plug-in Hybrid EV | Battery EV | Where Used |
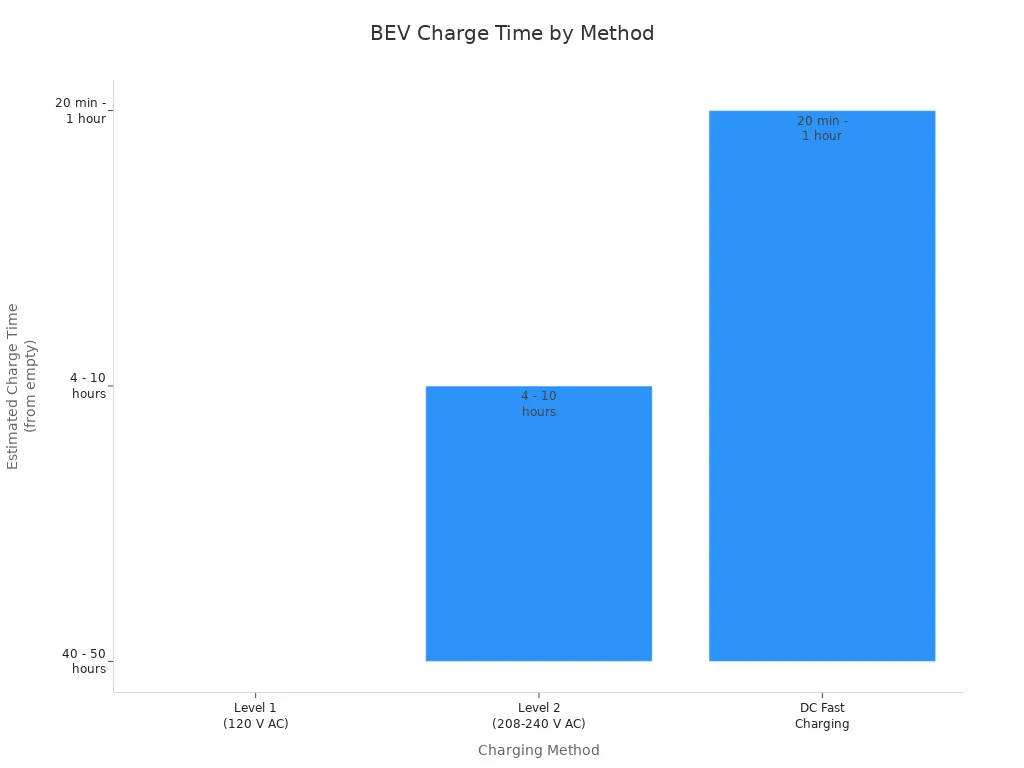
Level 1 (120V) | ~1 kW | 5-6 hours | 40-50 hours | Home |
Level 2 (240V) | 7-19 kW | 1-2 hours | 4-10 hours | Home, Public |
DC Fast Charging | 50-350 kW | N/A | 20-60 minutes (to 80%) | Public, Highways |
Many new EV drivers think charging always takes too long, but real-world experience shows that electric cars, electric motorcycles, and electric tricycles from Jinpeng make daily charging simple and efficient.
Key Takeaways
Electric cars charge at different speeds. The speed depends on the charger type. Level 1 chargers are slow. Level 2 chargers are faster. DC fast charging is the fastest.
Charging time depends on your battery size. It also depends on how full your battery is. The power your car and charger can use matters too.
Most EV owners charge at home overnight. They use Level 1 or Level 2 chargers. This is easy and works well for daily use.
DC fast chargers are good for quick charging on long trips. They are not good for daily charging.
Cold weather can make charging slower. Charging in a warm place helps. Charging after driving also helps your battery stay healthy.
Electric Car Charging Methods

When you start learning about electric car charging, you will see three main methods: Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging. Each method uses a different type of charger and offers different charging speeds. Understanding these options helps you choose the best way to keep your EV ready for the road.
Level 1 Charging Time
Level 1 charging uses a standard 120V household outlet. You can plug your electric car or plug-in hybrid directly into the wall, just like a phone or laptop. This method comes with most EVs and does not need special installation.
Level 1 chargers add about 3 to 5 miles of range per hour.
You can expect a full charge in 40 to 50+ hours for a battery electric car, or 6 to 12 hours for a plug-in hybrid.
Level 1 charging works best if you drive short distances each day, such as 30 to 40 miles, and can leave your car plugged in overnight.
Many people use Level 1 charging at home or at work, especially if they have a garage or a safe outdoor outlet.
Tip: Level 1 charging is simple and cost-effective for daily use, especially for smaller batteries or electric tricycles.
Level 2 Charging Time
Level 2 charging uses a 240V outlet, similar to what powers a clothes dryer. You may need a professional to install this charger at home, but it makes a big difference in charging speeds.
Level 2 chargers add about 20 to 40 miles of range per hour.
Most electric cars can reach a full charge in 4 to 10 hours.
Plug-in hybrids usually finish charging in 1 to 2 hours.
Level 2 charging is popular for home use, public parking lots, and workplaces.
Many EV owners rely on Level 2 charging overnight, so their car is ready each morning.
Level 2 charging is a great choice if you have a longer commute, a larger battery, or want to reduce your dependency on public charging stations. It also supports smart home features and can work with renewable energy.
DC Fast Charging Time
DC fast charging, also called Level 3, is the quickest way to charge your electric car. These chargers use direct current (DC) and deliver much higher power, from 50 kW up to 350 kW.
DC fast chargers can add up to 80% charge in just 20 to 60 minutes for most battery electric vehicles.
At 50 kW, charging from 20% to 80% takes about 52 minutes. At 100 kW, it drops to 26 minutes. At 150 kW, you can reach 80% in as little as 17 minutes.
Most plug-in hybrids do not support DC fast charging, but battery electric cars do.
You will find DC fast chargers at public stations, highway rest stops, and commercial locations.
Note: DC fast charging is perfect for road trips or when you need a quick top-up. Charging slows down after 80% to protect the battery, so most drivers use fast charging for quick stops, not daily charging.
Comparing Charging Methods
Here is a simple table to help you compare the three main charging methods for electric cars, plug-in hybrids, and other EVs like electric motorcycles and electric tricycles:
Charging Method | Voltage & Power | Range Added per Hour | Full Charge Time (BEV) | Full Charge Time (PHEV) | Where Used | Charger Cost |
Level 1 (120V) | 120V, 1.3-2.4 kW | 3-5 miles | 40-50+ hours | 6-12 hours | Home, Work | Minimal |
Level 2 (240V) | 240V, 3-19 kW | 20-40 miles | 4-10 hours | 1-2 hours | Home, Public, Work | $300-$1,000 + install |
DC Fast Charging | 50-350 kW (DC) | 60-1200 miles* | 20-60 minutes (to 80%) | N/A (most PHEVs not supported) | Public, Highways | $10,000+ |
*DC fast chargers add 10-20 miles per minute, so in one hour, you can add hundreds of miles, depending on your EV.
You can see that each charger type fits different needs. Level 1 works for daily home charging if you drive short distances. Level 2 is best for most EV owners who want faster charging at home or work. DC fast charging is ideal for long trips or quick stops at public fast charging stations.
Charging time depends on your vehicle’s battery size, the charger’s power, and how much charge you need. Most Jinpeng electric cars, electric motorcycles, and electric tricycles support Level 1 and Level 2 charging, making daily charging easy and flexible.
If you want to explore more about Jinpeng’s electric car lineup and find the right model for your needs, visit the Jinpeng Electric Car page.
Factors Affecting Charging Time

Charging an electric car is not just about plugging in and waiting. Several important factors decide how quickly your EV gets back on the road. Understanding these factors helps you plan your charging routine and choose the right charger for your needs.
Battery Size
The size of your EV’s battery plays a major role in how long charging takes. Larger batteries store more energy, so they need more time to fill up, especially on slower chargers. For example, a small electric car with a 40 kWh battery charges much faster than a large SUV with a 90 kWh battery when using the same charger.
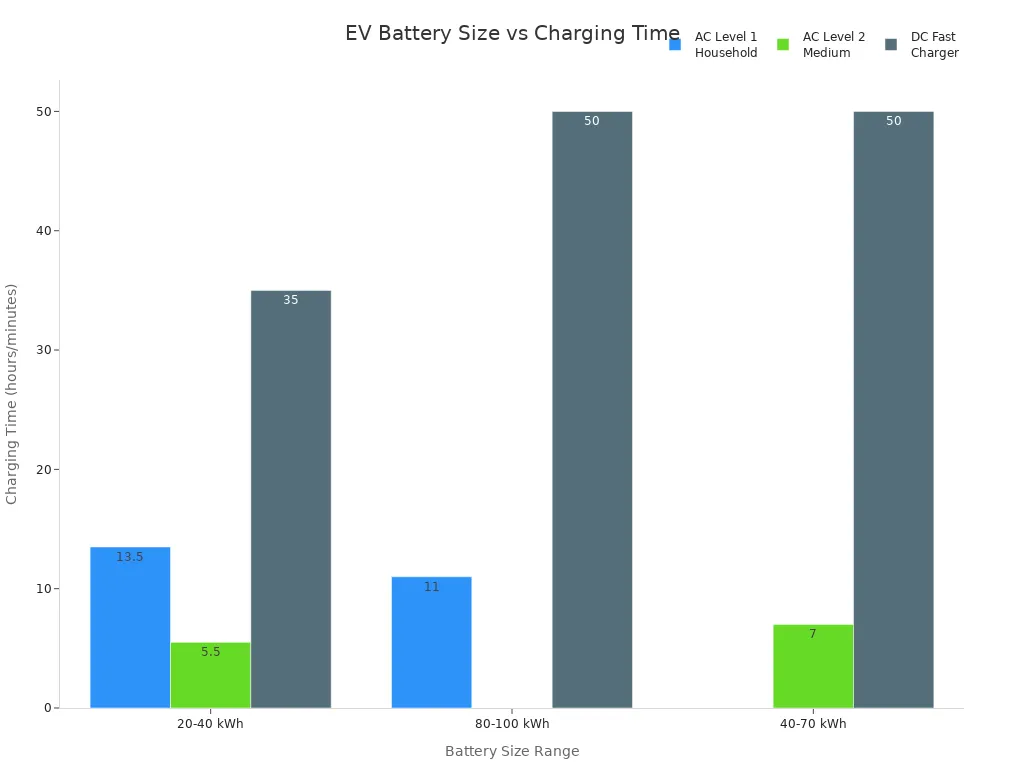
Battery Size Range | Typical EV Models | Charging Time on Level 1 (AC) | Charging Time on Level 2 (AC) | Charging Time on DC Fast Charger (to 80%) |
20-40 kWh | Jinpeng electric car, Nissan Leaf | 12-15 hours | 5-6 hours | 30-40 minutes |
40-70 kWh | Tesla Model 3, Volkswagen ID.4 | N/A | 6-8 hours | 40-60 minutes |
80-100 kWh | Tesla Model S, Audi e-tron | 10-12 hours | N/A | 40-60 minutes |
A small battery is perfect for city driving and short trips. You can charge it overnight at home. A larger battery gives you more range, which is great for long-distance travel, but it will take more hours to reach a full charge unless you use a fast charger.
Tip: If you drive mostly in the city, a smaller battery and a Level 2 charger can save you time and money.
State of Charge
The state of charge (SOC) means how full your battery is when you start charging. EV batteries charge fastest when the SOC is between 20% and 80%. When you plug in with a low battery, the charger works at its top speed. As the battery fills up, the charging speed slows down, especially after 80%. This protects the battery and helps it last longer.
You get the quickest charging when your battery is low.
Charging from 80% to 100% takes longer than charging from 20% to 80%.
Most drivers do not need to charge to 100% every time. Charging up to 80% is enough for daily use and keeps your battery healthy.
Note: For most Jinpeng electric cars and electric tricycles, charging from 20% to 80% is the sweet spot for both speed and battery life.
Vehicle and Charger Limits
Your EV and the charger must work together. Each has its own power limits. Even if you use a high-power charger, your vehicle will only accept as much power as it can handle. For example, if your electric car can take 7 kW, but you plug into a 22 kW charger, your car will still charge at 7 kW.
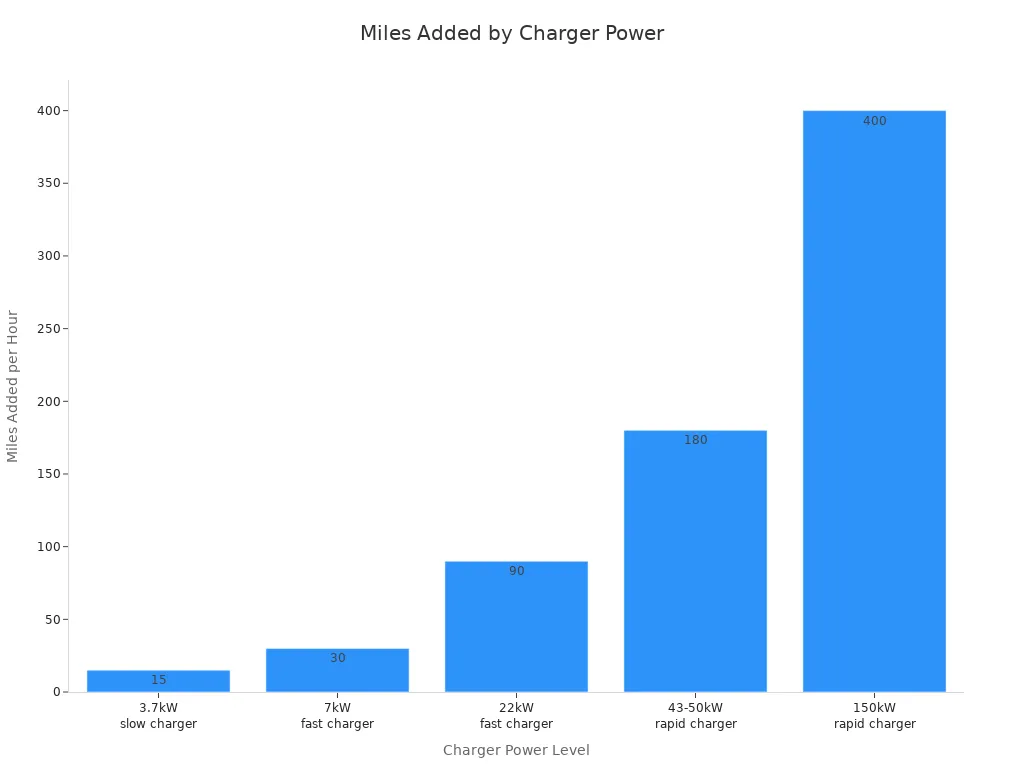
Charger Power Level | Approximate Miles Added per Hour |
3.7kW slow charger | Up to 15 miles |
7kW fast charger | Up to 30 miles |
22kW fast charger | Up to 90 miles |
43-50kW rapid charger | Up to 90 miles in 30 minutes |
150kW rapid charger | Up to 200 miles in 30 minutes |
You should always match your charger to your vehicle’s maximum charging speed. Using a much bigger charger does not make your EV charge faster if your car cannot accept the extra power. This is true for electric motorcycles and electric tricycles as well.
Temperature Effects
Temperature can change how fast your EV charges. Cold weather slows down charging because the battery needs to warm up before it can accept power quickly. In very cold conditions, charging can take up to three times longer than in warm weather. For example, at 32°F, an electric car may get 36% less charge after 30 minutes on a fast charger compared to charging at 77°F.
Cold weather increases charging time, especially at the start.
Hot weather affects range more than charging time, but extreme heat can still impact battery performance.
Many EVs, including Jinpeng models, use battery management systems to help control temperature and protect the battery.
Pro Tip: If you live in a cold climate, try to charge your EV in a garage or after driving when the battery is already warm.
Practical Example
Let’s compare charging times for a small electric car and a large SUV:
Charging Level | Power Output | Small EV (40 kWh) | Large EV (90 kWh) |
Level 1 | 2.3 kW | ~11 hours 36 mins | ~26 hours 5 mins |
Level 2 | 7.4 kW | ~3 hours 36 mins | ~8 hours 6 mins |
Level 2 | 22 kW | ~1 hour 8 mins | ~2 hours 27 mins |
Level 3 | 50 kW | ~32 minutes | ~1 hour 12 mins |
Level 3 | 100 kW | ~16 minutes | ~36 minutes |
You can see that a larger battery takes more hours to charge, even with a fast charger. This is why knowing your battery size, state of charge, and the limits of your vehicle and charger helps you plan your charging stops and avoid surprises.
Charging time depends on many factors, but with the right charger and a little planning, you can keep your Jinpeng electric car, electric tricycle, or electric motorcycle ready for every trip.
How Fast Do Electric Cars Charge
Range Added Per Hour
You may wonder how fast do electric cars charge in real life. The answer depends on the charging speed and the type of charger you use. Level 1 chargers, which use a standard household outlet, add about 4 to 5 miles of range per hour. Level 2 chargers, found at homes and public stations, usually add 20 to 25 miles per hour. DC fast chargers are the quickest, adding 200 to 400 miles per hour. This makes them perfect for long trips or quick stops.
Charging Level | Typical Range Added per Hour | Where Used |
Level 1 (120V) | 4–5 miles | Home, Work |
Level 2 (240V) | 20–25 miles | Home, Public, Work |
DC Fast Charging | 200–400+ miles | Public, Highways |
Tip: For most daily driving, Level 2 charging gives you the best balance of speed and convenience.
Real-World Charging Scenarios
You will likely use different charging methods depending on your routine. Most EV owners charge at home overnight. This method is simple and lets you wake up to a full battery every morning. If you drive a Jinpeng electric car, electric tricycle, or electric motorcycle, you can plug in when you get home and let the battery fill up while you sleep.
When you travel long distances, public DC fast chargers help you recharge quickly. You can stop for a short break and add enough range to keep going. Many drivers also use top-up charging. This means plugging in for short periods during the day, such as while shopping or at work. Top-up charging helps keep your battery healthy and reduces the need for long charging sessions.
Smart charging habits, like charging to 80% instead of 100%, protect your battery and make EV ownership easier. You can enjoy flexible charging options and keep your vehicle ready for any trip.
How to Fully Charge an Electric Car
Home Charging
You can fully charge an electric car at home using a Level 1 or Level 2 charger. Most people find charging at home simple and convenient. Here are the basic steps you follow:
Get your charging cable. This cable may come with your EV or your home charger.
Plug the cable into your car’s charging port. The port is usually on the front or side of your vehicle.
Start the charging session. At home, charging often begins automatically. In shared spaces, you may need to use an app or card.
Wait for the battery to reach full charge. Level 1 charging can take up to 30 hours. Level 2 charging usually takes 4 to 7 hours.
End the charging session before unplugging. Some chargers lock the cable during charging for safety.
Charging at home works best if you can leave your car plugged in overnight. This method is cost-effective and gives you full control over your charging routine. Many Jinpeng electric cars and electric tricycles support both Level 1 and Level 2 charging, making it easy to keep your vehicle ready for daily use.
Tip: Charging at home is the most affordable way to fully charge an electric car. You can wake up each morning with a full battery.
Public Charging
Public charging stations help you fully charge an electric car when you are away from home. You will find Level 2 chargers and DC fast charging options at many locations. Here is what you can expect:
Level 2 public chargers work like home chargers. They usually take 4 to 7 hours for a full charge.
DC fast charging stations can charge your EV to 80% in just 20 to 30 minutes. This is much faster than home charging.
Some Jinpeng electric tricycles and microcars support battery swapping. You can replace a low battery with a fully charged one in 2 to 4 minutes at special stations.
Charging Level | Typical Time to Full Charge | Where Used | Notes |
Level 2 (Public) | 4–7 hours | Shopping centers, parking lots | Similar to home Level 2 charging |
DC Fast Charging | 20–30 minutes (to 80%) | Highways, public stations | Best for quick top-ups |
Battery Swapping | 2–4 minutes | Select stations | Available for some Jinpeng vehicles |
Public charging is perfect for long trips or when you need a quick boost. You can find a charging station in many cities and along highways. For Jinpeng electric tricycles, battery swapping offers a fast and flexible solution, especially for delivery or commercial use.
Note: Charging times depend on your vehicle, charger type, and battery size. Fast charging at public stations is convenient, but charging at home remains the most cost-effective choice for most drivers.
You can charge many electric cars in just 20 minutes with a DC fast charger. At home, charging overnight is also easy. How fast your EV charges depends on battery size, charger type, and temperature. Check the table below to see how charging speeds and setups compare for your EV, electric tricycle, or electric motorcycle.
Charging Level | Speed (miles of range per hour) | Typical Use Case | Setup Requirement |
Level 1 Charging | 2-5 | Short daily commutes, backup | Standard 120-volt outlet |
Level 2 Charging | 10-25 | Daily charging at home/work | 240-volt outlet |
DC Fast Charging | 60-100 (in 20 minutes) | Long-distance travel, quick recharge | Dedicated DC fast charging stations |
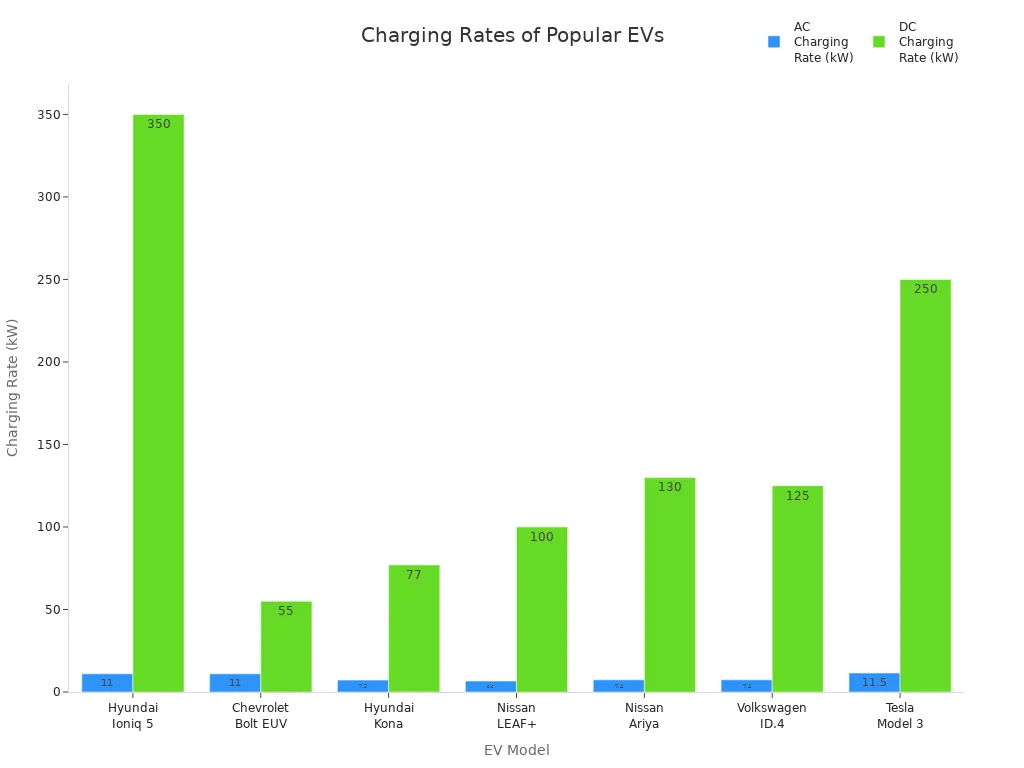
Charging an electric car works well for most people. You can pick the charging method that fits your life. Modern EVs give you lots of choices and make charging simple.
FAQ
How long does it take to charge a Jinpeng electric car at home?
Most Jinpeng electric cars charge at home in 4 to 10 hours with a Level 2 charger. Level 1 charging is much slower. It can take all night or even up to 30 hours.
Can I use public charging stations for my Jinpeng electric tricycle?
Yes, you can use many public Level 2 charging stations for your Jinpeng electric tricycle. Some models let you swap the battery. Swapping takes just a few minutes.
Does cold weather affect electric car charging time?
Yes, charging slows down in cold weather. Your electric car may need more time to charge in winter. Charging in a garage or after driving keeps the battery warmer.
What is the fastest way to charge a Jinpeng electric motorcycle?
A DC fast charger is the quickest way if your Jinpeng electric motorcycle supports it. Most people use Level 2 charging for daily rides.




















